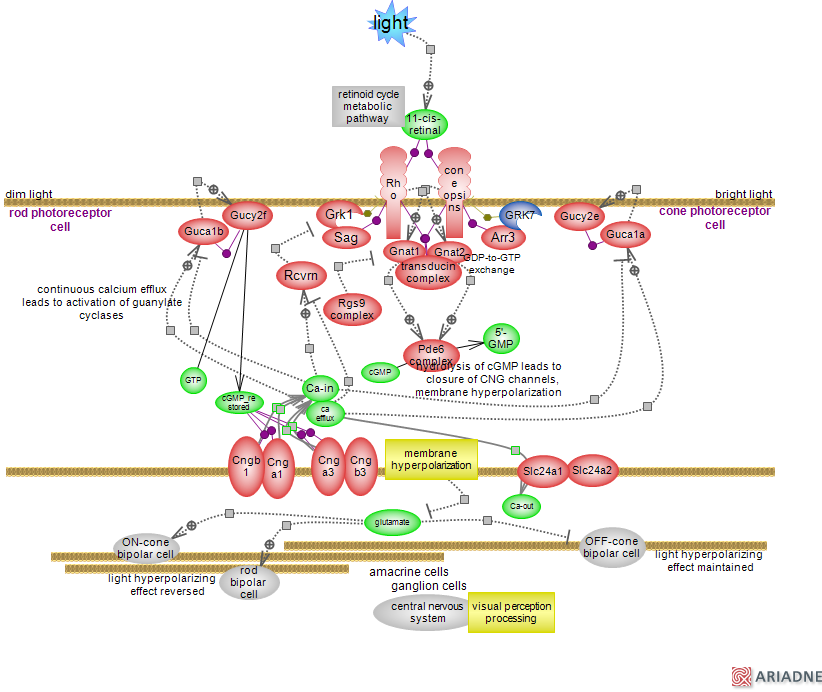
VISUAL PHOTOTRANSDUCTION PATHWAY (PW:0000962)
Description
Two types of photoreceptors in the vertebrate retina mediate the light response: the rods which mediate vision in dim light and the cones which mediate bright light and color vision. Both sense light with a visual pigment composed of vitamin A derived chromophore 11-cis retinal and a G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) to which the chromophore is covalently bound. Humans have one rod and three cones for long, medium- and short-waves. Rods and cones differ in their morphology, details of signaling and specific steps of chromophore regeneration. Overall, rods are very sensitive to light and respond to a single photon, the cones are less so. The mechanism of phototransduction on rod cells has been extensively studied; rhodopsin, the rod GPCR is considered a paradigm for the superfamily of 7 trans-membrane (7TM) GPCRs and the rhodopsin-like or A family/class in particular. Briefly, 11-cis retinal is buried in the core of the 7 TM; a lysine residue is the site for a protonated Schiff base linkage between receptor and ligand, further stabilized by nearby residues. In the absence of light 11-cis retinal acts as an inverse agonist by constraining the receptor in an inactive conformation. Upon light stimulation, the chromophore is isomerized to all-trans retinal, the Schiff base is deprotonated, a series of conformational changes in the photoreceptor follow and the isomerized choromophore is released. Rearrangement of TM5-TM6 opens up the binding site for the specific G protein transducin at the cytoplasmic site of the receptor. In the resting state, G proteins are heterotrimers consisting of alpha-GDP-bound, beta and gamma subunits; the alpha GTPase domain is conserved in all members of the G protein superfamily, including the small monomeric G proteins. The C-terminus of the alpha subunit is relatively flexible prior to binding, but adopts a helical structure subsequently; the conformational changes reverberate to the nucleotide binding site leading to release of GDP. Binding of GTP prompts dissociation of the GTP-alpha subunit from the receptor and the beta/gamma subunits. GTP-alpha interacts with and activate its target, the cyclic GMP phosphodiesterase (PDE). Active PDE hydrolyzes cGMP; the decrease in cGMP availability leads to closure of cGMP-gated cation channels resulting in membrane depolarization, decreased release of glutamate neurotransmitter and signaling to adjacent neurons. cGMP hydrolysis will continue for as long as G-alpha is GTP-bound. GTP hydrolysis occurs via the intrinsic GTPase activity of alpha transducin, further facilitated by the Rgs9 complex with GTPase-activating-protein activity (GAP). The signal, which is terminated via G protein inactivation, is also modulated at the level of the receptors. Specific kinases Grk1 and GRK7 (blue denotes human protein) phosphorylate the active photoreceptors which are then recognized by specific arrestin proteins and the interaction precludes binding of transducin to the active receptors. Light prompted closure of cation channels prevents calcium influx into the cell but not its efflux via the Na+/Ca2+, K+ exchanger of the Slc24 gene family. The overall decrease in intracellular calcium concentration provides several negative feedback loops resulting in restoration of cGMP levels and adjustment of photoreceptors light sensitivity usually referred to as 'light adaptation'. The guanylate cyclases, whose activity results in cGMP production, are constitutively bound to activator proteins (GCAPs), calcium binding proteins that inhibit the cyclases in the presence of calcium but stimulate them in its absence. Recoverin is another calcium binding protein; it inhibits Grk1 kinase activity in the presence of calcium and this effect is removed when calcium concentration decreases. Rods and cone cells synapse on bipolar (and horizontal) cells, in turn synapsing on amacrine and ganglion cells; the signal is relayed to the midbrain, the thalamus and the visual cortex where processing of visual perception and the aspects of visual experience take place. The cGMP-gated channel - a tetrameric complex belonging to the small family of cyclic-nucleotide-gated (CNG) cation channels is a non-selective cation channel; it does not get desensitized by ligands and maintains a steady inward current in darkness (dark current). In the absence of light the cells are sufficiently depolarized to allow for a sustained synaptic release of glutamate neurotransmitter which hyperpolarizes (inhibits) the ON-cone and rod and depolarizes (activates) the OFF-cone downstream bipolar cells. Glutamate, an excitatory neurotransmitter has an inhibitory effect on the ON-cone and rod bipolar cells; they express the metabotropic receptor Grm6, known as mGluR6, which is negatively coupled to a cation channel. Hyperpolarization of photoreceptor cells in response to light leads to decreased release of glutamate, reversing the hyperpolarizing 'sign' of light signal into a depolarizing one on these cells (decrease in glutamate and associated lack of activation of a specific G protein downstream of Grm6, further inactivated by its own GTPase activity in turn aided by a specific Rgs GAP complex, prompts the opening of the cation channel, possibly a member of the transient receptor potential [TRP] channels family). The sign is maintained at the OFF-cone cells which express the lower affinity ionotropic AMPA/kainite glutamate receptors and the cells are hyperpolarized. Thus, the separation of signals related to light increments (ON) and decrements (OFF) takes place at the first synapse of the retina. To sustain vision, all-trans retinal, resulting from the isomerization of the chromophore, needs to be converted back to the 11-cis isomer. This is accomplished through a series of reactions catalyzed by membrane-bound enzymes; the metabolic pathway is known as the retinoid or visual cycle. Visual phototransduction is a complex signaling pathway, continuously balancing the response to light and the modulation of that response. Mutations in a number of components in the visual phototransduction and retinoid cycle pathways have been linked to several human retinal degeneration and autosomal recessive diseases.
To see the ontology report for annotations, Gviewer and download, click here ;
to access a list of selected structures, click here .
[Click to see associated GO term - GO:0007602 map04774 ]...(less)
Pathway Diagram:
Genes in Pathway:
G
Arr3
arrestin 3
ISO
RGD
PMID:22074925 PMID:21824527 RGD:6893539 , RGD:6893556
NCBI chr X:69,739,959...69,752,300
G
Arrb1
arrestin, beta 1
IEA
KEGG rno:04744
NCBI chr 1:163,249,654...163,321,711
G
Arrb2
arrestin, beta 2
IEA
KEGG rno:04744
NCBI chr10:55,645,539...55,653,485
G
Calm1
calmodulin 1
IEA
KEGG rno:04744
NCBI chr 6:125,217,191...125,227,855
G
Calm2
calmodulin 2
IEA
KEGG rno:04744
NCBI chr 6:12,845,170...12,857,830
G
Calm3
calmodulin 3
IEA
KEGG rno:04744
NCBI chr 1:86,718,761...86,725,869
G
Calml3
calmodulin-like 3
IEA
KEGG rno:04744
NCBI chr17:71,329,438...71,333,068
G
Calml5
calmodulin-like 5
IEA
KEGG rno:04744
NCBI chr17:71,304,326...71,305,245
G
Cimip3
ciliary microtubule inner protein 3
ISO
RGD PMID:22074925 RGD:6893539
NCBI chr 9:21,058,433...21,080,642
G
Cnga1
cyclic nucleotide gated channel subunit alpha 1
TAS IEA
KEGG PMID:12087135 rno:04744, RGD:6893549
NCBI chr14:35,920,948...35,959,065
G
Cnga3
cyclic nucleotide gated channel subunit alpha 3
TAS
RGD
PMID:12087135 RGD:6893549
NCBI chr 9:46,943,353...46,989,862
G
Cngb1
cyclic nucleotide gated channel subunit beta 1
TAS IEA
KEGG PMID:12087135 rno:04744, RGD:6893549
NCBI chr19:9,732,646...9,798,864
G
Cngb3
cyclic nucleotide gated channel subunit beta 3
ISO
RGD
PMID:12087135 RGD:6893549
NCBI chr 5:37,543,903...37,792,030
G
Gnat1
G protein subunit alpha transducin 1
ISO IEA
KEGG PMID:22074925 rno:04744, RGD:6893539
NCBI chr 8:117,229,575...117,234,311
G
Gnat2
G protein subunit alpha transducin 2
ISO IEA
KEGG PMID:22074925 rno:04744, RGD:6893539
NCBI chr 2:198,414,568...198,431,532
G
Gnat3
G protein subunit alpha transducin 3
IEA
KEGG rno:04744
NCBI chr 4:18,054,551...18,104,332
G
Gnb1
G protein subunit beta 1
ISO IEA
KEGG PMID:22074925 rno:04744, RGD:6893539
NCBI chr 5:171,357,778...171,424,489
G
Gnb3
G protein subunit beta 3
ISO
RGD
PMID:22074925 RGD:6893539
NCBI chr 4:159,325,741...159,331,443
G
Gnb5
G protein subunit beta 5
ISO
RGD
PMID:22074925 RGD:6893539
NCBI chr 8:84,956,629...84,985,576
G
Gngt1
G protein subunit gamma transducin 1
ISO IEA
KEGG PMID:22074925 rno:04744, RGD:6893539
NCBI chr 4:32,960,945...32,963,930
G
Gngt2
G protein subunit gamma transducin 2
ISO
RGD
PMID:22074925 RGD:6893539
NCBI chr10:81,271,916...81,280,980
G
Grk1
G protein-coupled receptor kinase 1
ISO IEA
KEGG PMID:21903131 rno:04744, RGD:6893555
NCBI chr16:82,821,184...82,837,971
G
Guca1a
guanylate cyclase activator 1A
ISO IEA
KEGG PMID:22074925 rno:04744, RGD:6893539
NCBI chr 9:21,080,782...21,096,221
G
Guca1b
guanylate cyclase activator 1B
ISO IEA
KEGG PMID:22074925 rno:04744, RGD:6893539
NCBI chr 9:21,097,274...21,105,107
G
Gucy2d
guanylate cyclase 2D
IEA
KEGG rno:04744
NCBI chr 1:162,150,967...162,185,666
G
Gucy2e
guanylate cyclase 2E
ISO IEA
KEGG PMID:22074925 rno:04744, RGD:6893539
NCBI chr10:54,453,753...54,478,639
G
Gucy2f
guanylate cyclase 2F
ISO IEA
KEGG PMID:22074925 rno:04744, RGD:6893539
NCBI chr X:110,507,183...110,605,017
G
Opn1mw
opsin 1, medium wave sensitive
ISO
RGD
PMID:21704730 RGD:6893536
NCBI chr X:157,056,355...157,076,716
G
Opn1sw
opsin 1, short wave sensitive
ISO
RGD
PMID:21704730 RGD:6893536
NCBI chr 4:58,942,685...58,945,825
G
Pde6a
phosphodiesterase 6A
ISO IEA
KEGG PMID:15224133 rno:04744, RGD:6893540
NCBI chr18:56,947,249...57,019,015
G
Pde6b
phosphodiesterase 6B
ISO IEA
KEGG PMID:15224133 rno:04744, RGD:6893540
NCBI chr14:1,468,302...1,511,435
G
Pde6c
phosphodiesterase 6C
ISO
RGD
PMID:15224133 RGD:6893540
NCBI chr 1:245,322,015...245,377,874
G
Pde6g
phosphodiesterase 6G
ISO
RGD
PMID:15224133 RGD:6893540
NCBI chr10:106,219,849...106,224,496
G
Pde6h
phosphodiesterase 6H
ISO
RGD
PMID:15224133 RGD:6893540
NCBI chr 4:171,588,896...171,604,142
G
Rcvrn
recoverin
ISO IEA
KEGG PMID:22074925 rno:04744, RGD:6893539
NCBI chr10:52,887,667...52,895,413
G
Rgs9
regulator of G-protein signaling 9
ISO IEA
KEGG PMID:22074925 rno:04744, RGD:6893539
NCBI chr10:94,696,556...94,770,387
G
Rgs9bp
regulator of G protein signaling 9 binding protein
ISO
RGD
PMID:22074925 RGD:6893539
NCBI chr 1:97,386,326...97,387,039
G
Rho
rhodopsin
ISO IEA
KEGG PMID:21704730 rno:04744, RGD:6893536
NCBI chr 4:150,653,205...150,658,367
G
Sag
S-antigen visual arrestin
ISO
RGD
PMID:22074925 PMID:21824527 RGD:6893539 , RGD:6893556
NCBI chr 9:95,915,640...95,956,641
G
Slc24a1
solute carrier family 24 member 1
ISO IEA
KEGG PMID:18690016 rno:04744, RGD:6893550
NCBI chr 8:74,334,556...74,361,313
G
Slc24a2
solute carrier family 24 member 2
ISO
RGD
PMID:18690016 RGD:6893550
NCBI chr 5:106,543,867...106,787,810
G
Cnga1
cyclic nucleotide gated channel subunit alpha 1
ISO
RGD
PMID:20212494 RGD:8547536
NCBI chr14:35,920,948...35,959,065
G
Cngb1
cyclic nucleotide gated channel subunit beta 1
ISO
RGD
PMID:20212494 RGD:8547536
NCBI chr19:9,732,646...9,798,864
G
Guca1b
guanylate cyclase activator 1B
ISO
RGD
PMID:20212494 RGD:8547536
NCBI chr 9:21,097,274...21,105,107
G
Pde6a
phosphodiesterase 6A
ISO
RGD
PMID:20212494 RGD:8547536
NCBI chr18:56,947,249...57,019,015
G
Pde6b
phosphodiesterase 6B
ISO
RGD
PMID:20212494 RGD:8547536
NCBI chr14:1,468,302...1,511,435
G
Pde6g
phosphodiesterase 6G
ISO
RGD
PMID:20212494 RGD:8547536
NCBI chr10:106,219,849...106,224,496
G
Rho
rhodopsin
ISO
RGD
PMID:20212494 RGD:8547536
NCBI chr 4:150,653,205...150,658,367
G
Sag
S-antigen visual arrestin
ISO
RGD
PMID:20212494 RGD:8547536
NCBI chr 9:95,915,640...95,956,641
Pathway Gene Annotations
Disease Annotations Associated with Genes in the visual phototransduction pathway
Arr3 genetic disease , Myopia 26, X-Linked, Female-Limited , syndromic microphthalmia 5 Arrb1 Arteriovenous Fistula , colitis , congestive heart failure , Experimental Arthritis , liver cirrhosis , major depressive disorder , Transplant Rejection Arrb2 alcohol dependence , amphetamine abuse , Arteriovenous Fistula , brain infarction , drug psychosis , Experimental Arthritis , Experimental Liver Cirrhosis , Experimental Liver Neoplasms , glioblastoma , hepatocellular carcinoma , heroin dependence , hypertension , liver cirrhosis , metabolic dysfunction and alcohol associated liver disease , Myocardial Reperfusion Injury , nicotine dependence , opiate dependence , pain agnosia , portal hypertension , renal fibrosis , Transplant Rejection , type 2 diabetes mellitus Calm1 alcohol dependence , alcohol withdrawal syndrome , Alzheimer's disease , cannabis abuse , catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia , catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia 1 , catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia 4 , Cocaine-Related Disorders , long QT syndrome , long QT syndrome 14 , phencyclidine abuse , type 2 diabetes mellitus , Weight Gain Calm2 alcohol dependence , alcohol withdrawal syndrome , cannabis abuse , Cocaine-Related Disorders , COVID-19 , genetic disease , long QT syndrome , long QT syndrome 1 , long QT syndrome 15 , major depressive disorder , phencyclidine abuse , substance abuse , sudden infant death syndrome Calm3 alcohol dependence , alcohol withdrawal syndrome , familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy , long QT syndrome , long QT syndrome 1 , long QT syndrome 16 Calml3 hepatocellular carcinoma , Lung Neoplasms , Neoplasm Metastasis Calml5 Alzheimer's disease , dry eye syndrome Cimip3 Hereditary Eye Diseases Cnga1 retinitis pigmentosa , retinitis pigmentosa 49 Cnga3 achromatopsia , Achromatopsia 1 , achromatopsia 2 , achromatopsia 3 , color blindness , cone dystrophy , cone-rod dystrophy , Eye Abnormalities , fundus dystrophy , genetic disease , macular degeneration , optic atrophy Cngb1 fundus dystrophy , genetic disease , optic atrophy , retinitis pigmentosa , retinitis pigmentosa 45 , retinitis pigmentosa 49 Cngb3 achromatopsia , Achromatopsia 1 , achromatopsia 3 , color blindness , cone-rod dystrophy , Eye Abnormalities , fundus dystrophy , genetic disease , Leber congenital amaurosis , macular degeneration , optic atrophy , pathologic nystagmus , retinitis pigmentosa , Stargardt disease , Stargardt Disease 1 Gnat1 congenital stationary night blindness , congenital stationary night blindness 1C , congenital stationary night blindness 1G , congenital stationary night blindness autosomal dominant 3 , Experimental Diabetes Mellitus , fundus dystrophy , genetic disease , night blindness , retinitis pigmentosa Gnat2 achromatopsia , achromatopsia 4 , color blindness , cone dystrophy , Eye Abnormalities , fundus dystrophy , genetic disease Gnat3 Experimental Diabetes Mellitus , male infertility Gnb1 acute lymphoblastic leukemia , anxiety disorder , autism spectrum disorder , autosomal dominant intellectual developmental disorder , autosomal dominant intellectual developmental disorder 42 , cerebral palsy , cleft palate , congestive heart failure , depressive disorder , Developmental Disabilities , dystonia , epilepsy , epilepsy with generalized tonic-clonic seizures , Failure to Thrive , focal epilepsy , genetic disease , Growth Disorders , hypothyroidism , intellectual disability , Language Development Disorders , microcephaly , Muscle Hypotonia , myelodysplastic syndrome , Neurodevelopmental Disorders , pathologic nystagmus , strabismus Gnb3 carotid artery disease , congenital stationary night blindness , congenital stationary night blindness 1H , coronary artery disease , depressive disorder , diabetes mellitus , essential hypertension , familial hyperlipidemia , fundus dystrophy , genetic disease , hypertension , Insulin Resistance , obesity , Orthostatic Hypotension , type 2 diabetes mellitus , visual epilepsy , Weight Gain Gnb5 Colorectal Neoplasms , Developmental Disabilities , Fraser syndrome 3 , genetic disease , LANGUAGE DELAY AND ATTENTION DEFICIT-HYPERACTIVITY DISORDER/COGNITIVE IMPAIRMENT WITH OR WITHOUT CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIA , Lodder-Merla syndrome type 1 with impaired intellectual development and cardiac arrhythmia Gngt1 autism spectrum disorder , prostate cancer Gngt2 Experimental Liver Cirrhosis Grk1 congenital stationary night blindness , congestive heart failure , Experimental Diabetes Mellitus , fundus dystrophy , genetic disease , hereditary night blindness , Neuralgia , night blindness , Oguchi disease-2 , retinal disease Guca1a cone-rod dystrophy 14 , Hereditary Eye Diseases , retinitis pigmentosa Guca1b fundus dystrophy , Leber congenital amaurosis , retinitis pigmentosa , retinitis pigmentosa 48 Gucy2e choroidal sclerosis , cone dystrophy , cone-rod dystrophy , cone-rod dystrophy 6 , Congenital Stationary Night Blindness 1I , fundus dystrophy , genetic disease , Hereditary Optic Atrophies , Leber congenital amaurosis , Leber congenital amaurosis 1 , Leber congenital amaurosis 2 , leukodystrophy , macular degeneration , optic atrophy , pathologic nystagmus , retinitis pigmentosa , Vision Disorders Gucy2f retinal degeneration Opn1mw achromatopsia , blue cone monochromacy , red-green color blindness Opn1sw atrial fibrillation , blue color blindness Pde6a fundus dystrophy , genetic disease , Leber congenital amaurosis , retinitis pigmentosa , retinitis pigmentosa 43 , Usher syndrome Pde6b Animal Disease Models , cone-rod dystrophy , cone-rod dystrophy 1 , congenital stationary night blindness , congenital stationary night blindness autosomal dominant 2 , fundus dystrophy , genetic disease , High Myopia , macular degeneration , prostate cancer , retinal degeneration , retinitis pigmentosa , retinitis pigmentosa 40 Pde6c achromatopsia , Achromatopsia 1 , Achromatopsia 5 , amphetamine abuse , cone dystrophy , Cone Dystrophy 4 , cone-rod dystrophy , Eye Abnormalities , fundus dystrophy , genetic disease , optic atrophy Pde6g fundus dystrophy , retinitis pigmentosa , retinitis pigmentosa 57 Pde6h color blindness , cone-rod dystrophy 14 , fundus dystrophy , retinal cone dystrophy 3A Rgs9 bradyopsia , bradyopsia 1 , Drug-Induced Dyskinesia , fundus dystrophy , genetic disease , Hereditary Eye Diseases , Leber congenital amaurosis , optic atrophy , Parkinsonism , schizophrenia , substance-induced psychosis Rgs9bp bradyopsia , bradyopsia 2 , fundus dystrophy Rho Coats disease , cone-rod dystrophy , cone-rod dystrophy 14 , Congenital Hypomyelinating Neuropathy 2 , congenital stationary night blindness , congenital stationary night blindness autosomal dominant 1 , fundus albipunctatus , fundus dystrophy , genetic disease , night blindness , occult macular dystrophy , optic atrophy , primary autosomal recessive microcephaly 17 , retinal degeneration , retinitis pigmentosa , retinitis pigmentosa 4 , Stargardt disease , Stargardt Disease 1 Sag cone dystrophy , congenital stationary night blindness , fundus dystrophy , genetic disease , hereditary night blindness , Oguchi disease-1 , Oguchi disease-2 , retinitis pigmentosa , retinitis pigmentosa 47 , retinitis pigmentosa 96 , uveitis Slc24a1 Cerebral Hemorrhage , congenital stationary night blindness , congenital stationary night blindness 1D , congenital stationary night blindness autosomal dominant 2 , fundus dystrophy , genetic disease , retinitis pigmentosa
achromatopsia Cnga3 , Cngb3 , Gnat2 , Opn1mw , Pde6c Achromatopsia 1 Cnga3 , Cngb3 , Pde6c achromatopsia 2 Cnga3 achromatopsia 3 Cnga3 , Cngb3 achromatopsia 4 Gnat2 Achromatopsia 5 Pde6c acute lymphoblastic leukemia Gnb1 alcohol dependence Arrb2 , Calm1 , Calm2 , Calm3 alcohol withdrawal syndrome Calm1 , Calm2 , Calm3 Alzheimer's disease Calm1 , Calml5 amphetamine abuse Arrb2 , Pde6c Animal Disease Models Pde6b anxiety disorder Gnb1 Arteriovenous Fistula Arrb1 , Arrb2 atrial fibrillation Opn1sw autism spectrum disorder Gnb1 , Gngt1 autosomal dominant intellectual developmental disorder Gnb1 autosomal dominant intellectual developmental disorder 42 Gnb1 blue color blindness Opn1sw blue cone monochromacy Opn1mw bradyopsia Rgs9 , Rgs9bp bradyopsia 1 Rgs9 bradyopsia 2 Rgs9bp brain infarction Arrb2 cannabis abuse Calm1 , Calm2 carotid artery disease Gnb3 catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia Calm1 catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia 1 Calm1 catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia 4 Calm1 Cerebral Hemorrhage Slc24a1 cerebral palsy Gnb1 choroidal sclerosis Gucy2e cleft palate Gnb1 Coats disease Rho Cocaine-Related Disorders Calm1 , Calm2 colitis Arrb1 color blindness Cnga3 , Cngb3 , Gnat2 , Pde6h Colorectal Neoplasms Gnb5 cone dystrophy Cnga3 , Gnat2 , Gucy2e , Pde6c , Sag Cone Dystrophy 4 Pde6c cone-rod dystrophy Cnga3 , Cngb3 , Gucy2e , Pde6b , Pde6c , Rho cone-rod dystrophy 1 Pde6b cone-rod dystrophy 14 Guca1a , Pde6h , Rho cone-rod dystrophy 6 Gucy2e Congenital Hypomyelinating Neuropathy 2 Rho congenital stationary night blindness Gnat1 , Gnb3 , Grk1 , Pde6b , Rho , Sag , Slc24a1 congenital stationary night blindness 1C Gnat1 congenital stationary night blindness 1D Slc24a1 congenital stationary night blindness 1G Gnat1 congenital stationary night blindness 1H Gnb3 Congenital Stationary Night Blindness 1I Gucy2e congenital stationary night blindness autosomal dominant 1 Rho congenital stationary night blindness autosomal dominant 2 Pde6b , Slc24a1 congenital stationary night blindness autosomal dominant 3 Gnat1 congestive heart failure Arrb1 , Gnb1 , Grk1 coronary artery disease Gnb3 COVID-19 Calm2 depressive disorder Gnb1 , Gnb3 Developmental Disabilities Gnb1 , Gnb5 diabetes mellitus Gnb3 drug psychosis Arrb2 Drug-Induced Dyskinesia Rgs9 dry eye syndrome Calml5 dystonia Gnb1 epilepsy Gnb1 epilepsy with generalized tonic-clonic seizures Gnb1 essential hypertension Gnb3 Experimental Arthritis Arrb1 , Arrb2 Experimental Diabetes Mellitus Gnat1 , Gnat3 , Grk1 Experimental Liver Cirrhosis Arrb2 , Gngt2 Experimental Liver Neoplasms Arrb2 Eye Abnormalities Cnga3 , Cngb3 , Gnat2 , Pde6c Failure to Thrive Gnb1 familial hyperlipidemia Gnb3 familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy Calm3 focal epilepsy Gnb1 Fraser syndrome 3 Gnb5 fundus albipunctatus Rho fundus dystrophy Cnga3 , Cngb1 , Cngb3 , Gnat1 , Gnat2 , Gnb3 , Grk1 , Guca1b , Gucy2e , Pde6a , Pde6b , Pde6c , Pde6g , Pde6h , Rgs9 , Rgs9bp , Rho , Sag , Slc24a1 genetic disease Arr3 , Calm2 , Cnga3 , Cngb1 , Cngb3 , Gnat1 , Gnat2 , Gnb1 , Gnb3 , Gnb5 , Grk1 , Gucy2e , Pde6a , Pde6b , Pde6c , Rgs9 , Rho , Sag , Slc24a1 glioblastoma Arrb2 Growth Disorders Gnb1 hepatocellular carcinoma Arrb2 , Calml3 Hereditary Eye Diseases Cimip3 , Guca1a , Rgs9 hereditary night blindness Grk1 , Sag Hereditary Optic Atrophies Gucy2e heroin dependence Arrb2 High Myopia Pde6b hypertension Arrb2 , Gnb3 hypothyroidism Gnb1 Insulin Resistance Gnb3 intellectual disability Gnb1 LANGUAGE DELAY AND ATTENTION DEFICIT-HYPERACTIVITY DISORDER/COGNITIVE IMPAIRMENT WITH OR WITHOUT CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIA Gnb5 Language Development Disorders Gnb1 Leber congenital amaurosis Cngb3 , Guca1b , Gucy2e , Pde6a , Rgs9 Leber congenital amaurosis 1 Gucy2e Leber congenital amaurosis 2 Gucy2e leukodystrophy Gucy2e liver cirrhosis Arrb1 , Arrb2 Lodder-Merla syndrome type 1 with impaired intellectual development and cardiac arrhythmia Gnb5 long QT syndrome Calm1 , Calm2 , Calm3 long QT syndrome 1 Calm2 , Calm3 long QT syndrome 14 Calm1 long QT syndrome 15 Calm2 long QT syndrome 16 Calm3 Lung Neoplasms Calml3 macular degeneration Cnga3 , Cngb3 , Gucy2e , Pde6b major depressive disorder Arrb1 , Calm2 male infertility Gnat3 metabolic dysfunction and alcohol associated liver disease Arrb2 microcephaly Gnb1 Muscle Hypotonia Gnb1 myelodysplastic syndrome Gnb1 Myocardial Reperfusion Injury Arrb2 Myopia 26, X-Linked, Female-Limited Arr3 Neoplasm Metastasis Calml3 Neuralgia Grk1 Neurodevelopmental Disorders Gnb1 nicotine dependence Arrb2 night blindness Gnat1 , Grk1 , Rho obesity Gnb3 occult macular dystrophy Rho Oguchi disease-1 Sag Oguchi disease-2 Grk1 , Sag opiate dependence Arrb2 optic atrophy Cnga3 , Cngb1 , Cngb3 , Gucy2e , Pde6c , Rgs9 , Rho Orthostatic Hypotension Gnb3 pain agnosia Arrb2 Parkinsonism Rgs9 pathologic nystagmus Cngb3 , Gnb1 , Gucy2e phencyclidine abuse Calm1 , Calm2 portal hypertension Arrb2 primary autosomal recessive microcephaly 17 Rho prostate cancer Gngt1 , Pde6b red-green color blindness Opn1mw renal fibrosis Arrb2 retinal cone dystrophy 3A Pde6h retinal degeneration Gucy2f , Pde6b , Rho retinal disease Grk1 retinitis pigmentosa Cnga1 , Cngb1 , Cngb3 , Gnat1 , Guca1a , Guca1b , Gucy2e , Pde6a , Pde6b , Pde6g , Rho , Sag , Slc24a1 retinitis pigmentosa 4 Rho retinitis pigmentosa 40 Pde6b retinitis pigmentosa 43 Pde6a retinitis pigmentosa 45 Cngb1 retinitis pigmentosa 47 Sag retinitis pigmentosa 48 Guca1b retinitis pigmentosa 49 Cnga1 , Cngb1 retinitis pigmentosa 57 Pde6g retinitis pigmentosa 96 Sag schizophrenia Rgs9 Stargardt disease Cngb3 , Rho Stargardt Disease 1 Cngb3 , Rho strabismus Gnb1 substance abuse Calm2 substance-induced psychosis Rgs9 sudden infant death syndrome Calm2 syndromic microphthalmia 5 Arr3 Transplant Rejection Arrb1 , Arrb2 type 2 diabetes mellitus Arrb2 , Calm1 , Gnb3 Usher syndrome Pde6a uveitis Sag Vision Disorders Gucy2e visual epilepsy Gnb3 Weight Gain Calm1 , Gnb3