PROTEIN C ANTICOAGULANT PATHWAY (PW:0000480)
Description
In response to vascular injury, the hemostatic system triggers platelet aggregation and initiation of the coagulation cascade, primary and secondary hemostasis, respectively, to prevent bleeding. The coagulation cascade initiated via tissue factor - the extrinsic pathway, or contact - the intrinsic pathway, converges into a common pathway leading to formation of insoluble fibrin clots. A fibrinolytic cascade follows coagulation to lyse fibrin and protect against blood clotting. Several anticoagulant systems are in place to tightly regulate coagulation. An important system is represented by the protein C anticoagulant pathway, whose roles beyond the control of coagulation are emerging. The anticoagulant actions prevent thrombosis while the more recently discovered cytoprotective actions prevent vascular damage and stress.
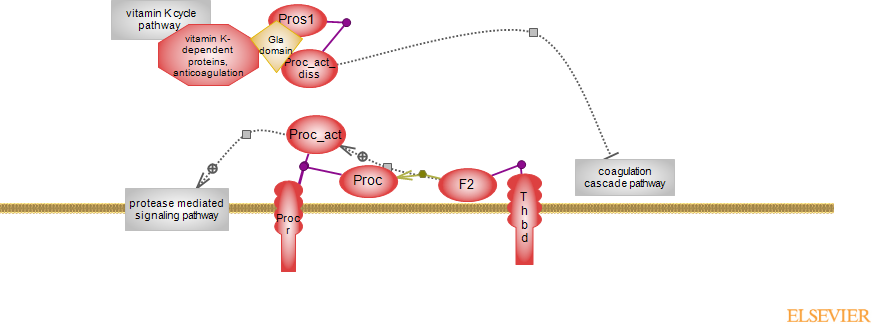
Proteolytic activation of protein C (Proc) is carried out by thrombin/F2 bound to the membrane receptor thrombomodulin (Thbd). F2 is the last protease of the coagulation cascade; its binding to Thbd obscures the procoagulant site - exosite 1, converting it to an anticoagulant factor. Binding of protein C to its receptor, Procr, anchors it to the endothelial surface, allowing for its presentation to the thrombin-thrombomodulin complex and subsequent activation. As an anticoagulant, activated protein C (Proc_act) dissociates from Procr (Proc_act_diss) and, assisted by protein S cofactor, effectively inactivates coagulation cofactors 5a and 8a. F8a is the cofactor for coagulation factor 9a in the 'tenase complex'; F5a is the cofactor for coagulation factor 10a in the 'thrombinase complex'. Both protein C and protein S cofactor are vitamin K-dependent (VKD) proteins. Vitamin K serves as a cofactor in the reaction that modifies specific glutamine (Glu) residues to gamma-carboxyglutamate (Gla) residues. Glas (10 to 12) in the amino terminal Gla domain (
click to access the PFAM entry ) mediate the reversible, calcium-dependent binding to negatively charged phospholipids (phosphatidylserine or phosphatidic acid) of membranes. With each modified residue, a reduced form of vitamin K is oxidized and is then converted back, to provide the necessary cofactor for the next reaction - the metabolic pathway is known as the vitamin K cycle. Also VKD proteins are the coagulation factors F2, F7, F9 and F10, and several other proteins. The localization of coagulation factors and regulators of coagulation at/near sites of vascular injury is crucial for proper hemostatic function.
In a different role, Proc_act bound to Epcr prompts cytoprotective actions via activation of protease-activated receptors (PARs). PARs are G protein-coupled receptors (GPCR) involved in many responses and can elicit distinct downstream events depending on the identity of the protease and cellular environment; the alternative outcomes are referred to as 'biased signaling'. Of the four members, primarily Par1/F2R, but also Par3/F2Rl2, are targets. These receptors are also targets of thrombin/F2; however, the effects elicited by Proc and F2 are not only different, they are divergent. Cytoprotective effects elicited by Proc-Epcr include antiapoptotic, anti-inflammatory and endothelial barrier stabilization. In contrast, thrombin-elicited effects are pro-inflammatory and barrier destabilizing. The alternative outcomes - 'biased signaling', result from cleavage of receptors at different sites by different proteases, yielding new, and distinct N-terminal tethered agonists, associated conformations and allosteric modulations, as well as distinct conformations receptors can have in the membrane environment. The Proc cleavage site in Par1 is different from the 'canonical' cleavage site of thrombin.
Given the many roles Proc in association with its receptor/cofactor can play, alterations in protein C pathway can have profound negative consequences.
To see the ontology report for annotations, GViewer, and download, click here ...(less)
Pathway Diagram:
Genes in Pathway:
G
F2
coagulation factor II, thrombin
ISS ISO
RGD
PMID:12970121 PMID:23809128 RGD:1578508 , RGD:11352294
NCBI chr 3:98,051,958...98,065,246
G
F5
coagulation factor V
ISO
RGD
PMID:15257017 RGD:1580373
NCBI chr13:79,046,657...79,116,247
G
Proc
protein C, inactivator of coagulation factors Va and VIIIa
TAS ISO
RGD
PMID:14995995 PMID:23809128 RGD:1578389 , RGD:11352294
NCBI chr18:24,038,596...24,049,061
G
Procr
protein C receptor
ISS ISO
RGD
PMID:12970121 PMID:23809128 RGD:1578508 , RGD:11352294
NCBI chr 3:164,714,727...164,718,994
G
Pros1
protein S
ISS ISO
RGD
PMID:12970121 PMID:23809128 RGD:1578508 , RGD:11352294
NCBI chr11:13,676,310...13,757,858
G
Thbd
thrombomodulin
ISO
RGD
PMID:23809128 RGD:11352294
NCBI chr 3:156,316,526...156,320,178
Pathway Gene Annotations
Disease Annotations Associated with Genes in the protein C anticoagulant pathway
F2 acquired angioedema , Acute Coronary Syndrome , Acute Lung Injury , allergic rhinitis , Alzheimer's disease , appendicitis , asthma , atherosclerosis , atopic dermatitis , autoimmune hepatitis , bacterial pneumonia , blood coagulation disease , brain edema , Brain Injuries , brain ischemia , bullous pemphigoid , calcium oxalate nephrolithiasis , carotid stenosis , celiac disease , Cerebral Hemorrhage , cerebral infarction , cerebral palsy , Chagas disease , chronic obstructive pulmonary disease , clear cell renal cell carcinoma , Congenital Prothrombin Deficiency , Contusions , coronary artery disease , COVID-19 , Crohn's disease , dengue disease , Diabetic Nephropathies , disseminated intravascular coagulation , end stage renal disease , Endotoxemia , Experimental Arthritis , Experimental Diabetes Mellitus , eye disease , factor VIII deficiency , Familial Amyloid Polyneuropathies , familial Mediterranean fever , Femur Head Necrosis , genetic disease , glomerulonephritis , Habitual Abortions , hemolytic-uremic syndrome , hemophilia B , Hemorrhage , Hemorrhagic Shock , hepatitis C , hepatocellular carcinoma , hereditary angioedema , herpes zoster , high grade glioma , Human Viral Hepatitis , Huntington's disease , Hyperalgesia , hyperglycemia , hyperhomocysteinemia , Hypertrophy , intracranial sinus thrombosis , ischemic stroke , Kidney Calculi , Knee Osteoarthritis , left ventricular failure , leptospirosis , liver cirrhosis , Liver Failure , Mesenteric Ischemia , metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease , middle cerebral artery infarction , myocardial infarction , Neoplasm Metastasis , nephrosis , Nerve Degeneration , obesity , ovarian cancer , Paratuberculosis , Pediatric Crohn's Disease , portal vein thrombosis , pre-eclampsia , prostate cancer , prothrombin deficiency , pulmonary embolism , pulmonary fibrosis , Reperfusion Injury , retinal vein occlusion , rheumatoid arthritis , schizophrenia , sensorineural hearing loss , Sepsis , Septic Peritonitis , sickle cell anemia , Spinal Cord Injuries , steatotic liver disease , stroke , systemic lupus erythematosus , systemic scleroderma , Thromboembolism , thrombophilia , thrombophilia due to thrombin defect , thrombosis , toxic shock syndrome , type 2 diabetes mellitus , ulcerative colitis , urinary bladder cancer , Urinary Calculi , urticaria , vascular skin disease , Venous Thromboembolism , Venous Thrombosis , Ventricular Fibrillation F5 Acute Liver Failure , Behcet's disease , blood coagulation disease , brain ischemia , breast cancer , Budd-Chiari syndrome , cerebral infarction , cholesteatoma , Colonic Neoplasms , colorectal adenoma , COVID-19 , Dysarthria , Dyspnea , end stage renal disease , Endotoxemia , Experimental Liver Cirrhosis , factor V deficiency , familial adenomatous polyposis , Femur Head Necrosis , Fetal Death , genetic disease , Habitual Abortions , Hemorrhage , hemorrhagic disease , hepatitis , Hereditary Thrombophilia , Hirschsprung's disease , hypereosinophilic syndrome , ischemic stroke , liver cirrhosis , membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis , Mesenteric Ischemia , myocardial infarction , Myocardial Ischemia , non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy , Peritoneal Fibrosis , portal hypertension , pre-eclampsia , prostate cancer , pulmonary embolism , pulmonary fibrosis , pulmonary hypertension , retinal artery occlusion , retinal vein occlusion , sagittal sinus thrombosis , sensorineural hearing loss , Sepsis , Septic Peritonitis , stroke , thrombocytopenia , Thromboembolism , thrombophilia due to activated protein C resistance , thrombophilia due to thrombin defect , thrombosis , Venous Thromboembolism , Venous Thrombosis Proc Acute Experimental Pancreatitis , acute kidney failure , Acute Lung Injury , antiphospholipid syndrome , Arteritis , asthma , autosomal dominant thrombophilia due to protein C deficiency , autosomal recessive thrombophilia due to protein C deficiency , blood coagulation disease , central retinal vein occlusion , cerebral infarction , cerebral palsy , Congenital Thrombotic Disease, due to Protein C Deficiency , disseminated intravascular coagulation , Endotoxemia , Female Infertility , genetic disease , Hearing Loss, Noise-Induced , Heat Stroke , hypertension , Intestinal Reperfusion Injury , Liver Reperfusion Injury , Lung Reperfusion Injury , middle cerebral artery infarction , myocardial infarction , osteonecrosis , placental abruption , pre-eclampsia , protein C deficiency , pulmonary embolism , purpura fulminans , Sepsis , Spinal Cord Reperfusion Injury , Thromboembolism , thrombophilia , thrombophilia due to activated protein C resistance , thrombosis , thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura , toxic shock syndrome , Venous Thromboembolism , Venous Thrombosis Procr Acute Experimental Pancreatitis , acute kidney failure , Acute Lung Injury , basal cell carcinoma , carotid stenosis , coronary artery disease , Experimental Liver Cirrhosis , Inflammation , malaria , Myocardial Reperfusion Injury , Peripheral Nerve Injuries Pros1 adult respiratory distress syndrome , autosomal dominant thrombophilia due to protein S deficiency , autosomal recessive thrombophilia due to protein S deficiency , blood coagulation disease , cerebral infarction , Diabetic Nephropathies , Experimental Liver Cirrhosis , fundus dystrophy , genetic disease , hemorrhagic disease , juvenile rheumatoid arthritis , nephrotic syndrome type 1 , optic atrophy , protein S deficiency , pulmonary embolism , sagittal sinus thrombosis , Stevens-Johnson syndrome , Thromboembolism , thrombophilia due to activated protein C resistance , thrombophlebitis , thrombosis , vascular disease , Venous Thromboembolism , Venous Thrombosis Thbd acute kidney failure , Acute Liver Failure , Acute Lung Injury , acute promyelocytic leukemia , adult respiratory distress syndrome , Alzheimer's disease , ankylosing spondylitis , asthma , atypical hemolytic-uremic syndrome , B-Cell Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia , Brain Injuries , brain small vessel disease , carotid artery thrombosis , cerebral infarction , coronary artery disease , Coronary Disease , Crohn's disease , dermatomyositis , disseminated intravascular coagulation , Drug-Related Side Effects and Adverse Reactions , end stage renal disease , Endotoxemia , Endotoxin-Induced Uveitis , Experimental Arthritis , Experimental Liver Cirrhosis , familial combined hyperlipidemia , familial Mediterranean fever , genetic disease , granulomatosis with polyangiitis , Habitual Abortions , Heat Stroke , hemolytic-uremic syndrome , hemorrhagic disease , Hyperalgesia , hypertension , hypothyroidism , idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis , impotence , Inflammation , Insulin Resistance , ischemia , juvenile rheumatoid arthritis , kidney disease , liver disease , lung non-small cell carcinoma , Metabolic Syndrome , Multiple Organ Failure , myocardial infarction , obesity , Painful Neuropathy , pulmonary embolism , pulmonary hypertension , Reperfusion Injury , rheumatoid arthritis , Sepsis , severe acute respiratory syndrome , Spinal Cord Injuries , Stomach Neoplasms , stroke , Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome , systemic lupus erythematosus , thrombocytopenia , Thromboembolism , thrombophilia , thrombophilia due to thrombomodulin defect , thrombosis , thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura , type 1 diabetes mellitus , type 2 diabetes mellitus , ulcerative colitis
acquired angioedema F2 Acute Coronary Syndrome F2 Acute Experimental Pancreatitis Proc , Procr acute kidney failure Proc , Procr , Thbd Acute Liver Failure F5 , Thbd Acute Lung Injury F2 , Proc , Procr , Thbd acute promyelocytic leukemia Thbd adult respiratory distress syndrome Pros1 , Thbd allergic rhinitis F2 Alzheimer's disease F2 , Thbd ankylosing spondylitis Thbd antiphospholipid syndrome Proc appendicitis F2 Arteritis Proc asthma F2 , Proc , Thbd atherosclerosis F2 atopic dermatitis F2 atypical hemolytic-uremic syndrome Thbd autoimmune hepatitis F2 autosomal dominant thrombophilia due to protein C deficiency Proc autosomal dominant thrombophilia due to protein S deficiency Pros1 autosomal recessive thrombophilia due to protein C deficiency Proc autosomal recessive thrombophilia due to protein S deficiency Pros1 B-Cell Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Thbd bacterial pneumonia F2 basal cell carcinoma Procr Behcet's disease F5 blood coagulation disease F2 , F5 , Proc , Pros1 brain edema F2 Brain Injuries F2 , Thbd brain ischemia F2 , F5 brain small vessel disease Thbd breast cancer F5 Budd-Chiari syndrome F5 bullous pemphigoid F2 calcium oxalate nephrolithiasis F2 carotid artery thrombosis Thbd carotid stenosis F2 , Procr celiac disease F2 central retinal vein occlusion Proc Cerebral Hemorrhage F2 cerebral infarction F2 , F5 , Proc , Pros1 , Thbd cerebral palsy F2 , Proc Chagas disease F2 cholesteatoma F5 chronic obstructive pulmonary disease F2 clear cell renal cell carcinoma F2 Colonic Neoplasms F5 colorectal adenoma F5 Congenital Prothrombin Deficiency F2 Congenital Thrombotic Disease, due to Protein C Deficiency Proc Contusions F2 coronary artery disease F2 , Procr , Thbd Coronary Disease Thbd COVID-19 F2 , F5 Crohn's disease F2 , Thbd dengue disease F2 dermatomyositis Thbd Diabetic Nephropathies F2 , Pros1 disseminated intravascular coagulation F2 , Proc , Thbd Drug-Related Side Effects and Adverse Reactions Thbd Dysarthria F5 Dyspnea F5 end stage renal disease F2 , F5 , Thbd Endotoxemia F2 , F5 , Proc , Thbd Endotoxin-Induced Uveitis Thbd Experimental Arthritis F2 , Thbd Experimental Diabetes Mellitus F2 Experimental Liver Cirrhosis F5 , Procr , Pros1 , Thbd eye disease F2 factor V deficiency F5 factor VIII deficiency F2 familial adenomatous polyposis F5 Familial Amyloid Polyneuropathies F2 familial combined hyperlipidemia Thbd familial Mediterranean fever F2 , Thbd Female Infertility Proc Femur Head Necrosis F2 , F5 Fetal Death F5 fundus dystrophy Pros1 genetic disease F2 , F5 , Proc , Pros1 , Thbd glomerulonephritis F2 granulomatosis with polyangiitis Thbd Habitual Abortions F2 , F5 , Thbd Hearing Loss, Noise-Induced Proc Heat Stroke Proc , Thbd hemolytic-uremic syndrome F2 , Thbd hemophilia B F2 Hemorrhage F2 , F5 hemorrhagic disease F5 , Pros1 , Thbd Hemorrhagic Shock F2 hepatitis F5 hepatitis C F2 hepatocellular carcinoma F2 hereditary angioedema F2 Hereditary Thrombophilia F5 herpes zoster F2 high grade glioma F2 Hirschsprung's disease F5 Human Viral Hepatitis F2 Huntington's disease F2 Hyperalgesia F2 , Thbd hypereosinophilic syndrome F5 hyperglycemia F2 hyperhomocysteinemia F2 hypertension Proc , Thbd Hypertrophy F2 hypothyroidism Thbd idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis Thbd impotence Thbd Inflammation Procr , Thbd Insulin Resistance Thbd Intestinal Reperfusion Injury Proc intracranial sinus thrombosis F2 ischemia Thbd ischemic stroke F2 , F5 juvenile rheumatoid arthritis Pros1 , Thbd Kidney Calculi F2 kidney disease Thbd Knee Osteoarthritis F2 left ventricular failure F2 leptospirosis F2 liver cirrhosis F2 , F5 liver disease Thbd Liver Failure F2 Liver Reperfusion Injury Proc lung non-small cell carcinoma Thbd Lung Reperfusion Injury Proc malaria Procr membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis F5 Mesenteric Ischemia F2 , F5 metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease F2 Metabolic Syndrome Thbd middle cerebral artery infarction F2 , Proc Multiple Organ Failure Thbd myocardial infarction F2 , F5 , Proc , Thbd Myocardial Ischemia F5 Myocardial Reperfusion Injury Procr Neoplasm Metastasis F2 nephrosis F2 nephrotic syndrome type 1 Pros1 Nerve Degeneration F2 non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy F5 obesity F2 , Thbd optic atrophy Pros1 osteonecrosis Proc ovarian cancer F2 Painful Neuropathy Thbd Paratuberculosis F2 Pediatric Crohn's Disease F2 Peripheral Nerve Injuries Procr Peritoneal Fibrosis F5 placental abruption Proc portal hypertension F5 portal vein thrombosis F2 pre-eclampsia F2 , F5 , Proc prostate cancer F2 , F5 protein C deficiency Proc protein S deficiency Pros1 prothrombin deficiency F2 pulmonary embolism F2 , F5 , Proc , Pros1 , Thbd pulmonary fibrosis F2 , F5 pulmonary hypertension F5 , Thbd purpura fulminans Proc Reperfusion Injury F2 , Thbd retinal artery occlusion F5 retinal vein occlusion F2 , F5 rheumatoid arthritis F2 , Thbd sagittal sinus thrombosis F5 , Pros1 schizophrenia F2 sensorineural hearing loss F2 , F5 Sepsis F2 , F5 , Proc , Thbd Septic Peritonitis F2 , F5 severe acute respiratory syndrome Thbd sickle cell anemia F2 Spinal Cord Injuries F2 , Thbd Spinal Cord Reperfusion Injury Proc steatotic liver disease F2 Stevens-Johnson syndrome Pros1 Stomach Neoplasms Thbd stroke F2 , F5 , Thbd Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome Thbd systemic lupus erythematosus F2 , Thbd systemic scleroderma F2 thrombocytopenia F5 , Thbd Thromboembolism F2 , F5 , Proc , Pros1 , Thbd thrombophilia F2 , Proc , Thbd thrombophilia due to activated protein C resistance F5 , Proc , Pros1 thrombophilia due to thrombin defect F2 , F5 thrombophilia due to thrombomodulin defect Thbd thrombophlebitis Pros1 thrombosis F2 , F5 , Proc , Pros1 , Thbd thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura Proc , Thbd toxic shock syndrome F2 , Proc type 1 diabetes mellitus Thbd type 2 diabetes mellitus F2 , Thbd ulcerative colitis F2 , Thbd urinary bladder cancer F2 Urinary Calculi F2 urticaria F2 vascular disease Pros1 vascular skin disease F2 Venous Thromboembolism F2 , F5 , Proc , Pros1 Venous Thrombosis F2 , F5 , Proc , Pros1 Ventricular Fibrillation F2