 |
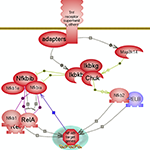
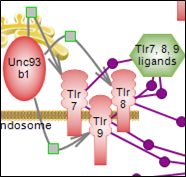
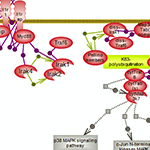
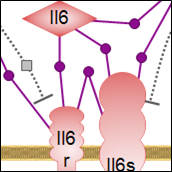
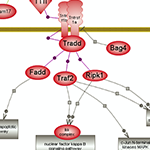
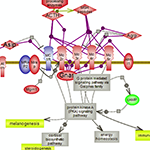
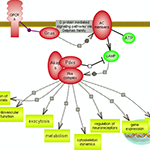
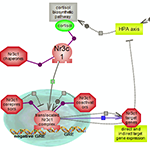
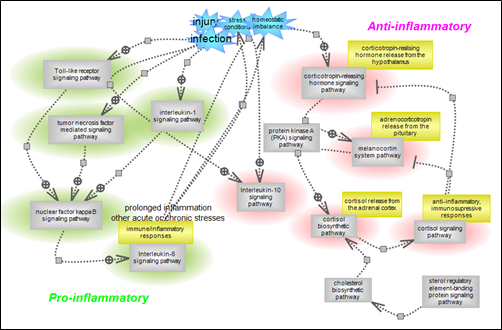
Living systems are exquisitely adroit at maintaining homeostasis despite constantly being challenged by environmental changes and stresses. One aspect involves rapid immune responses and the initiation of various pathways that underlie or relate to them. The other aspect relates to the timely suppression of these responses which, if prolonged, could become harmful, by prompting the pathways that counteract or control them. Nuclear factor kappa B signaling downstream of inflammatory cytokines, Toll-like receptors and pro-inflammatory interleukins signaling prompted by infection and/or stresses result in the expression of many genes involved in immune and inflammatory responses along with cell survival, proliferation and differentiation. On the other hand, the hypothalamus- pituitary-adrenal axis (HPA), via a relay of pathways, prompts the expression of cortisol or glucocorticoids whose signaling plays essential roles in the regulation of many important biological processes. Cortisol promotes the expression of anti-inflammatory proteins while repressing the expression of pro-inflammatory ones, and also providing a negative feedback loop for the HPA axis.In addition, the inflammatory response itself via both its stimuli and effects prompts the expression of the anti-inflammatory interleukins such as Il-10 and its subsequent signaling. A delicately balanced network of inter-related pathways and connecting regulatory loops underlie the pro- and anti- responses to maintain overall homeostasis.
Click here to explore the pro-inflammatory Nf-kappaB, Toll-like receptor, interleukins and related signaling pathways suite. Click here to explore the pathway suite for the anti-inflammatory hypothalamus- pituitary-adrenal axis (HPA), interleukin-10 and related pathways. |