Pathways of the HPA axis: |
||||
Corticotropin-releasing hormone signaling pathway |
Melanocortin system pathway |
|||
 |
 |
|||
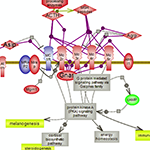
| Activation of the HPA axis triggers the release of corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) whose signaling via G-protein coupled receptors leads to activation of the protein kinase A (PKA) pathway and expression of the POMC gene. Click here to explore the details of this important pathway. | Melanocortin peptides generated from processing of the POMC gene product set in motion the melanocortin receptors. Adrenocorticotropin (ACTH) is the sole ligand of receptor type 2 and the signaling pathway(s) set in motion culminate with the release of the glucocorticoid cortisol steroid hormone. Click here to explore the complex features of melanocortin system signaling. | |||
Protein kinase A (PKA) signaling pathway |
||
 |
||
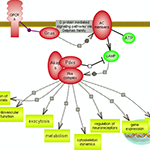
| Protein kinase A (PKA) signaling is a widely-used intracellular pathway downstream of adenylyl cyclase activating heterotrimeric G proteins of the Galpha family. The receptors for CRH and melanocortin peptides couple to this family. Click here to explore the details of this important signaling relay. |
Cortisol biosynthetic pathway |
Cortisol signaling pathway |
|||
 |
 |
|||
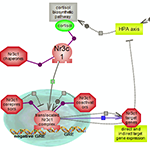
| Biosynthesis of cortisol happens primarily in the adrenal cortex in response to activation of the HPA axis. Click here to explore the details of this important metabolic pathway. | Cortisol signaling via its receptor plays important roles in many aspects of cellular and tissue physiology, is a potent anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive agent and provides a negative regulatory feedback loop to the HPA axis. Click here to explore the pathway involving this steroid hormone receptor. |
|||
| Return to page top | ||||
HPA axis-related pathways and anti-inflammatory interleukin-10 signaling: |
||||||
Cholesterol biosynthetic pathway |
Sterol regulatory element-binding protein signaling pathway |
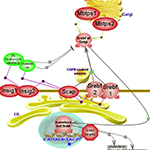
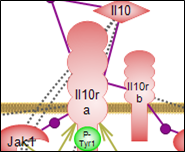
Interleukin-10 signaling pathway |
||||
 |
 |
 |
||||
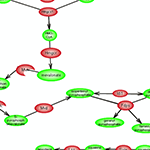
| Cholesterol, an essential component of cell membranes and lipids rafts, is also the precursor for the synthesis of steroid hormones and bile acids. The de novo synthesis of this 27 carbon lipid molecule from an initial 2 carbon precursor requires some 30 reactions and its levels are tightly regulated. Click here to explore this complex metabolic pathway. |
Sterol regulatory element-binding protein signaling regulates lipid and cholesterol homeostasis. Click here to explore this important pathway mediated by the SREBP transcription factors. | The anti-inflammatory interleukin-10 is expressed in many immune cells and while the signaling mechanisms accounting for it are not well understood, interleukin-6 and -12 pathways may be amongst those involved. Pathogenic microorganisms can also induce Il-10. Click here to explore this important signaling pathway. |
||||
| Return to page top |























