Balancing Blood Pressure Regulatory Mechanisms Pathway Suite Network
Click here to explore the Mechanisms Mediating and Pertinent to Increased Blood Pressure Pathway Suite.
Click here to explore the Mechanisms Mediating and Pertinent to Decreased Blood Pressure Pathway Suite.
Click here to explore the Mechanisms Mediating and Pertinent to Both Increased and Decreased Blood Pressure Pathway Suite.
Mechanisms Mediating and Pertinent to Increased Blood Pressure Pathway Suite
| Angiotensin II signaling pathway via AT1 receptor | Aldosterone signaling pathway | Aldosterone biosynthetic pathway |
| Angiotensin II is probably the most potent of the biologically active peptides generated by the renin-angiotensin system. Signaling via receptor type 1 activates a number of intracellular cascades and promotes vasoconstriction and hormone release, among others. Click here to explore this important signaling pathway. | Aldosterone signaling via its nuclear receptor promotes the expression of target genes with important roles in renal sodium reabsorption. Click here to examine this essential signaling pathway. | Aldosterone is the main C21 mineralocorticoid; like all steroid hormones it is derived from cholesterol and its synthesis takes place in the cortex of the adrenal gland. Click here to explore this important metabolic pathway. |
Cholesterol Biosynthesis and Regulation |
Anti-hypertensive Drugs |
||
| Cholesterol biosynthetic pathway | Losartan drug pathway | Statin drug pathway | |
| The synthesis of cholesterol requires more than 30 reactions to produce the 27-carbon molecule from the initial 2-carbon acetyl-CoA building block, and the exact sequence of final events is yet to be established. Click here to explore this complex metabolic pathway. | Signaling by the sterol regulatory element-binding protein transcription factors (Srebf) plays crucial roles in lipid homeostasis. Essential enzymes of cholesterol and fatty acid biosynthesis are among their target genes. Click here to explore this important metabolic pathway. | Losartan is an angiotensin II receptor type specific antagonist used in the treatment of hypertension and heart failure. Click here to explore the overall losartan drug pathway from which one can link to the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics drug pathways. | Statins are competitive inhibitors of the enzyme involved in the rate-determining step of the cholesterol biosynthetic pathway and are used in the prevention of cardiovascular diseases. Click here to explore the overall statin pathway from which one can link to the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics drug pathways. |
Return to Suite Network overview
Mechanisms Mediating and Pertinent to Decreased Blood Pressure Pathway Suite
| Kallikrein-kinin cascade pathway | Kinin signaling pathway | Angiotensin II signaling pathway via AT2 receptor |
| The kallilkrein-kinin cascade generates several active kinins from the precursor kininogen. Their signaling has important downstream effects for a number of organs and tissues. The cascade is intimately connected to the coagulation and classical complement pathways. Click here to explore this important system. | Kinin signaling activates several intracellular pathways to elicit vasodilation, inflammatory and pain responses. Click here to explore this complex signaling pathway. | Angiotensin II is probably the most potent of the biologically active peptides generated by the renin-angiotensin system. Signaling via receptor type 2 activates a number of intracellular cascades and promotes vasodilation and natriuresis, among other processes. Click here to explore this aspect of angiotensin II signaling. |
Return to Suite Network overview
Mechanisms Mediating and Pertinent to Both Increased and Decreased Blood Pressure Pathway Suite
| Renin-angiotensin cascade pathway | Angiotensin II signaling pathway | Protein kinase C (PKC) signaling pathway |
| The renin-angiotensin cascade generates several active peptides from the inactive angiotensinogen precursor. Their signaling engages distinct receptors and downstream pathways to elicit a broad spectrum of effects. Click here to explore this complex pathway. | Angiotensin II is probably the most potent of the biologically active peptides generated by the renin-angiotensin system. It elicits distinct responses through signaling via receptor types 1 and 2. Click here to explore the array of effects prompted by this peptide. | Protein kinase C (PKC) signaling is triggered by the Galphaq mediated signal transduction downstream of various G-protein coupled receptors. The upstream activation of phospholipases leads to the production of diacyl-glycerol (DAG) and inositol trisphosphate (IP3) and the latter prompts the release of calcium from intracellular stores. Both DAG and calcium activate members of PKC which then impact on many cellular processes. Click here to explore this important intracellular signaling pathway. |
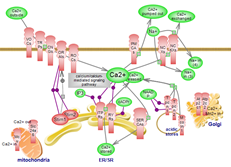
| Calcium transport pathway | Calcium/calcium-mediated signaling pathway |
| Calcium permeates almost every aspect of cellular function. Its provision and timely removal, buffering and sensing mediate the homeostasis of this versatile element. Calcium transport and signaling are intimately connected; together they are components of the ‘calcium signaling kit’. Click here to explore the complex transport axis, click here to examine the elaborate signaling axis of this system. | |
Click here to examine the Calcium Homeostasis Pathway Suite
Return to Suite Network overview