Nuclear factor kappa B signaling pathway |
Toll-like receptor signaling pathway
|
Interleukin 1 signaling pathway |
||
 |
|
|||
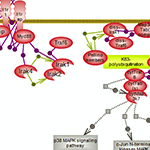
| Nuclear factor kappa B signaling results in the expression of many genes involved in the immune and inflammatory responses along with cell survival, proliferation and differentiation, and many upstream signaling pathways converge on its activation. Click here to explore this important signaling pathway. |
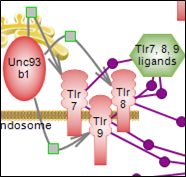
Toll-like receptors represent a first line of defense that responds to a variety of exogenous and also endogenous stress molecules. This causes NF-kappaB signaling and also some of the MAPK cascades to be initiated. Click here to explore this important defense system. |
Interleukin-1 signaling plays important roles in innate and adaptive immunity and is subject to tight control. The signaling initiated by this potent cytokine activates Nf-kappaB and MAPK cascades. Click here to explore this complex signaling system. |
||
| Interleukin-6 signaling pathway |
Tumor necrosis factor signaling pathway |
|
|
||
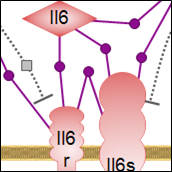
| Interleukin-6, the best characterized member of a family of cytokines, is involved in immune responses, inflammation, development, and the hematopoietic and nervous systems. Il-6 signaling triggers Jak-Stat and the Raf/Mek/Erk MAPK cascade. Click here to explore the elements of the Il-6 pathway. |
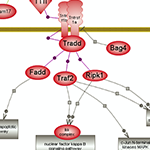
The tumor necrosis factor signaling pathway plays pivotal roles in immunity, cell proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis. While also being involved in the extrinsic apoptotic pathway, Tnf’s primary role is pro-inflammatory and pro-growth and the major conduit is activation of Nf-kappaB signaling. Click here to explore the many facets of the Tnf signaling pathway. |
|
| Return to page top |