Doxorubicin Pathway Suite
|
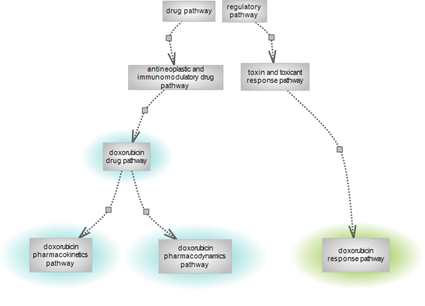
Doxorubicin is a widely used antineoplastic drug for the treatment of several solid tumors, leukemias and lymphomas. However, it can elicit potent cardiotoxic side effects, eventually leading to heart failure. While the overall aspects can be seen in the ‘doxorubicin drug pathway’ diagram page, the individual pathway entries reside in different nodes of the pathway ontology. The doxorubicin drug pathways are under the ‘antineoplastic and immunomodulatory drug pathway’ parent term in the drug pathway node. The ‘doxorubicin response pathway’ is under the ‘toxin and toxicant response pathway’ parent term in the regulatory pathway node. Toxins and toxicants, naturally produced by an organism or made by man, respectively, can be any substance/compound including drugs, the exposure to which induces a toxic effect. |
|
Doxorubicin drug pathway
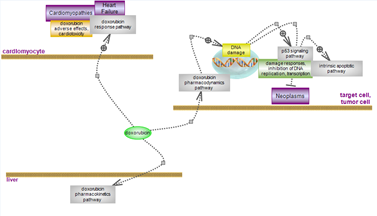 |
Doxorubicin response pathway
 |
| Doxorubicin is a widely-used antineoplastic drug for the treatment of several solid tumors, leukemias and lymphomas. However, it can elicit potent cardiotoxic side effects, eventually leading to heart failure. Click here to see the overall aspects of doxorubicin-related pathways. |
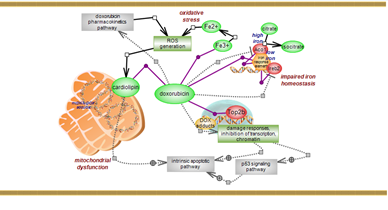
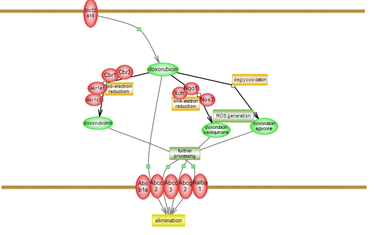
The severe cardiotoxic effects of doxorubicin could result from formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), impaired iron homeostasis and mitochondrial dysfunction. Click here to investigate the details. |
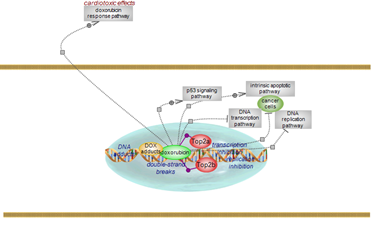
Doxorubicin pharmacodynamics pathway
 |
Doxorubicin pharmacokinetics pathway
 |
| Doxorubicin forms DNA adducts and its major effect is ‘trapping’ of topoisomerase type 2 in topoisomerase-DNA cleavage complexes, thus blocking the resealing of strands. Click here to examine this doxorubicin pathway. |
Doxorubicin uptake, elimination and processing are components of drug pharmacokinetics. Click here to explore the details. |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|