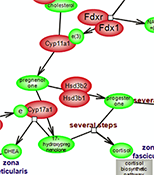
Steroid hormones, including the estrogens, androgens, mineralocorticoids and glucocorticoids, are comprised of molecules built around a common 4-ring structure derived from cholesterol. These vital hormones carry out a variety of diverse functions including controlling gender-specific phenotypes and secondary sex characteristics, regulating blood pressure and sodium uptake, stress adaptation, and modulating the metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins and lipids. The biosynthesis and release of steroid hormones are tightly regulated by the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis, with the biosynthetic process controlled chronically by changes in steroidogenic gene expression or acutely though delivery of the cholesterol precursor to the site of synthesis. Choose any of the links below to start exploring these vital pathways.