Pathway Suite for the Glucose Homeostasis-related Regulatory and Signaling Pathways
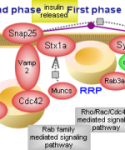
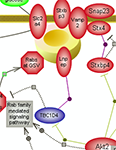
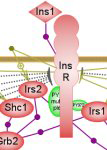
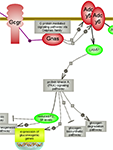
Glucose is a vital cellular fuel and constitutes the main energy source for the brain. The levels of glucose on both a cellular and a systemic scale are controlled by a complex network of metabolic, regulatory and signaling pathways. This suite of interactive pathway diagrams covers signaling and regulatory pathways pertinent to glucose homeostasis.
Click here to explore the metabolic pathways involved in glucose oxidation and conversion which also contribute to the delicate balance of glucose homeostasis in the body.
Disregulation of a number of glucose homeostasis-related metabolic, regulatory and signaling pathways has been linked to Type 2 Diabetes. Click here to explore the Type 2 Diabetes Pathway Suite for more information on pathways of relevance to this condition.
To link to the Diabetes Disease Portal, click here